Methane emissions in the United States have continued their downward trend from 2005 levels according to the Environmental Protection Agency’s 2021 Greenhouse Gas Inventory (GHGI). In fact, total U.S. greenhouse gas emissions continue to decline despite increased production and consumption of oil and natural gas. As the EPA explains:
“This decrease was driven largely by a decrease in emissions from fossil fuel combustion resulting from a decrease in total energy use in 2019 compared to 2018 and a continued shift from coal to natural gas and renewables in the electric power sector.”
Key Takeaways
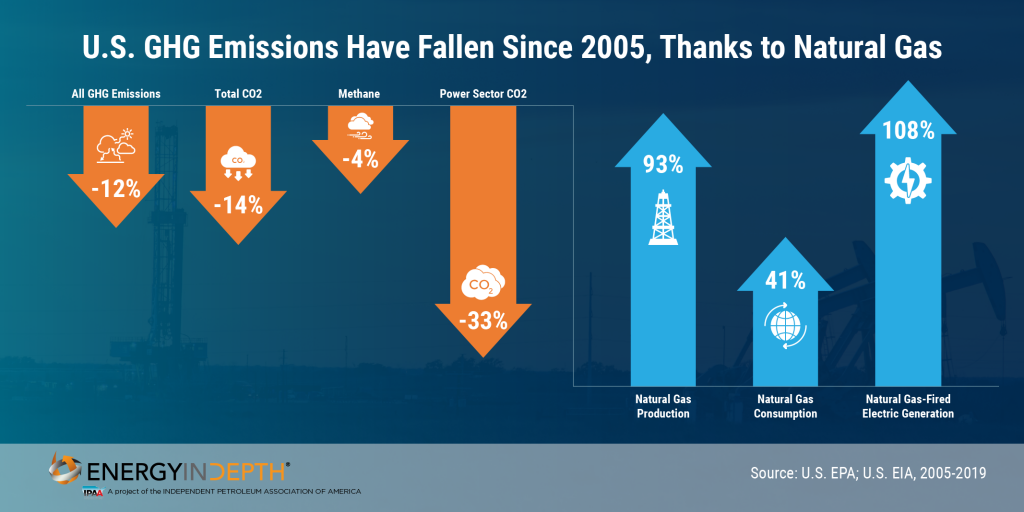
Total CO2 equivalent (Mmt CO2Eq) of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions dropped 11.6 percent from 2005 and methane emissions are down 16.6 percent since 1990 despite record production of oil and natural gas.

The 17 percent drop in oil and gas methane emissions can be contributed to the industry’s investments in reducing leaks and improving pipeline infrastructure. Methane emissions fell by 69 percent in natural gas distribution systems, and decreased 35 percent in natural gas transmission and storage.
These astonishing decreases occurred while the industry added more than 370,000 miles of new gas pipeline since 1990 to support a 62 percent increase in national demand.
U.S. Power Sector Emissions Continue to Fall
The U.S. power sector accounts for a sizable portion of the increased demand since 2005. The power sector doubled its intake of natural gas and saw emissions decline 33 percent.

As a recent Berkeley Labs report found, natural gas is responsible for approximately 48 percent of the sector’s emissions reductions since 2005.
Net emissions reduction from increased natural gas use also meant a decrease in carbon intensity. According to the GHGI:
“Decreases in natural gas prices and the associated increase in natural gas generation, particularly between 2005 and 2019, was one of the main drivers of the recent fuel switching and decrease in electric power sector carbon intensity.”
The power sector’s carbon intensity has decreased 16 percent since 1990.
GHGI Findings and Climate Goals
The oil and natural gas industry is leading emissions reduction across the national portfolio laid out in the EPA’s Greenhouse Gas Inventory. The industry’s investment in greenhouse gas mitigation technologies between 2000 and 2016 totaled $108.2 billion and the end results are apparent in GHGI reports year after year.
The industry is building on years of success and helping to provide for a low carbon future. The work of independent producers has reduced their methane emissions and helped the power sector lead the nation in carbon reduction. And with natural gas’s reliability, the power sector is able to increase its share of renewables, contributing to continued emissions reduction. As the Independent Petroleum Association of America recently explained:
“Due to the production of clean, efficient natural gas, the United States continues to be a world leader in reducing emissions that contribute to climate change. IPAA and our members are committed to reducing methane emissions and are also supportive of climate mitigation programs such as carbon capture and sequestration programs that hold the potential to significantly reduce CO2 emissions in the atmosphere. IPAA member companies are constantly innovating and improving our exploration and production methods.”