The Environmental Protection Agency’s 2022 Greenhouse Gas Inventory shows that U.S. methane emissions have continued to fall, even with increases in domestic energy consumption and production.
This is a testament to the efforts of the U.S. oil and natural gas industry to decrease emissions from operations and infrastructure, and the shift to natural gas for power generation which has played a major role in emissions reductions.
Total U.S. greenhouse gas emissions are down 20 percent since 2005, including continued reductions of both CO2 and methane.

Key takeaways
Total CO2 equivalent (Mmt CO2Eq) of methane from petroleum and natural gas systems dropped by 15 percent despite rampant increases of oil and natural gas production.

The significant decline in oil and gas methane emissions is heavily influenced by the industries recent investments in technological advancements that help detect and limit methane emissions, and a commitment to reduce routine flaring. For example, the 2021 Environmental Partnership report found that members have replaced tens of thousands of pieces of equipment to prevent leaks and conducted hundreds of thousands of surveys and inspections since 2017.

U.S. Power Sector Emissions Continue to Decline
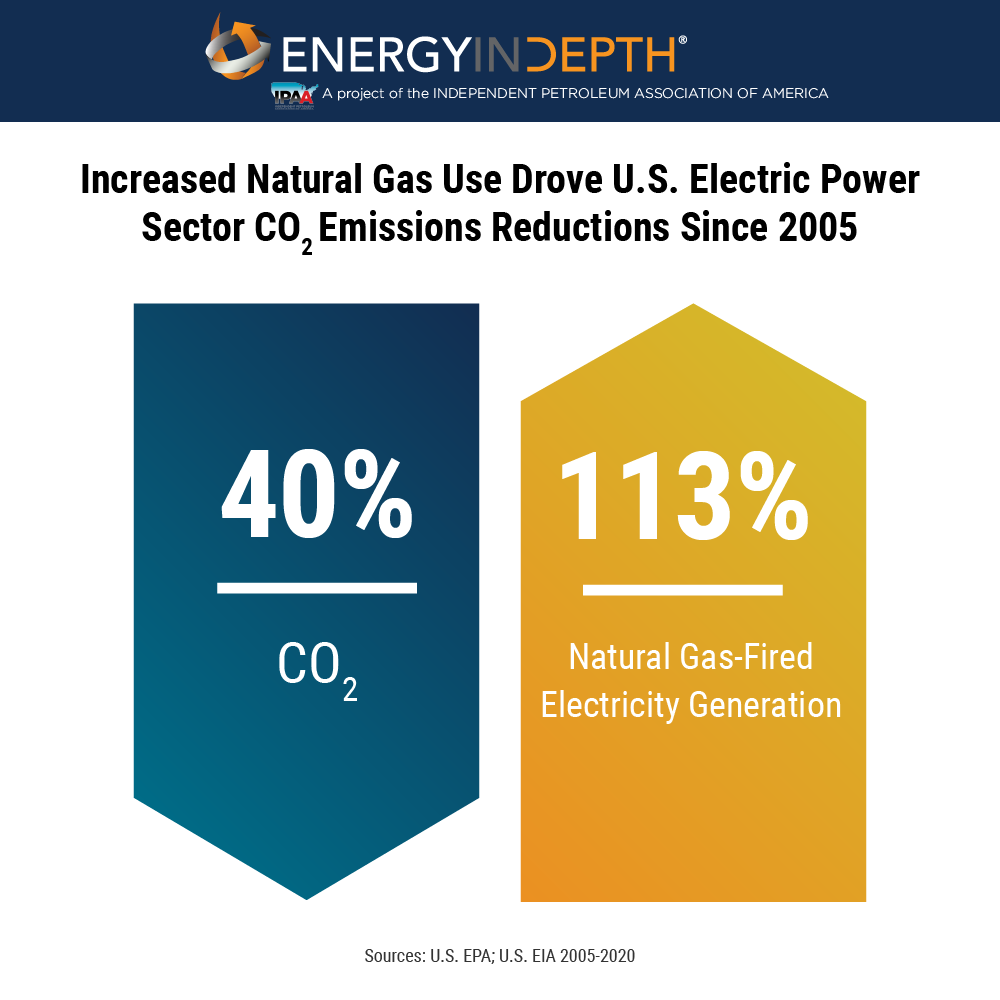
The U.S. power sector has embraced natural gas as more coal and other facilities have retired in recent years. Since 2005, the sector has decreased emissions by a whopping 40 percent – which the Energy Information Administration has largely credited to the switch to natural gas.
The U.S. oil and gas industry continues to invest in not only leak detection and monitoring to reduce emissions, but in innovations like carbon capture and hydrogen that will enable the United States to continue powering the world – and continue to reduce its environmental footprint in the process.